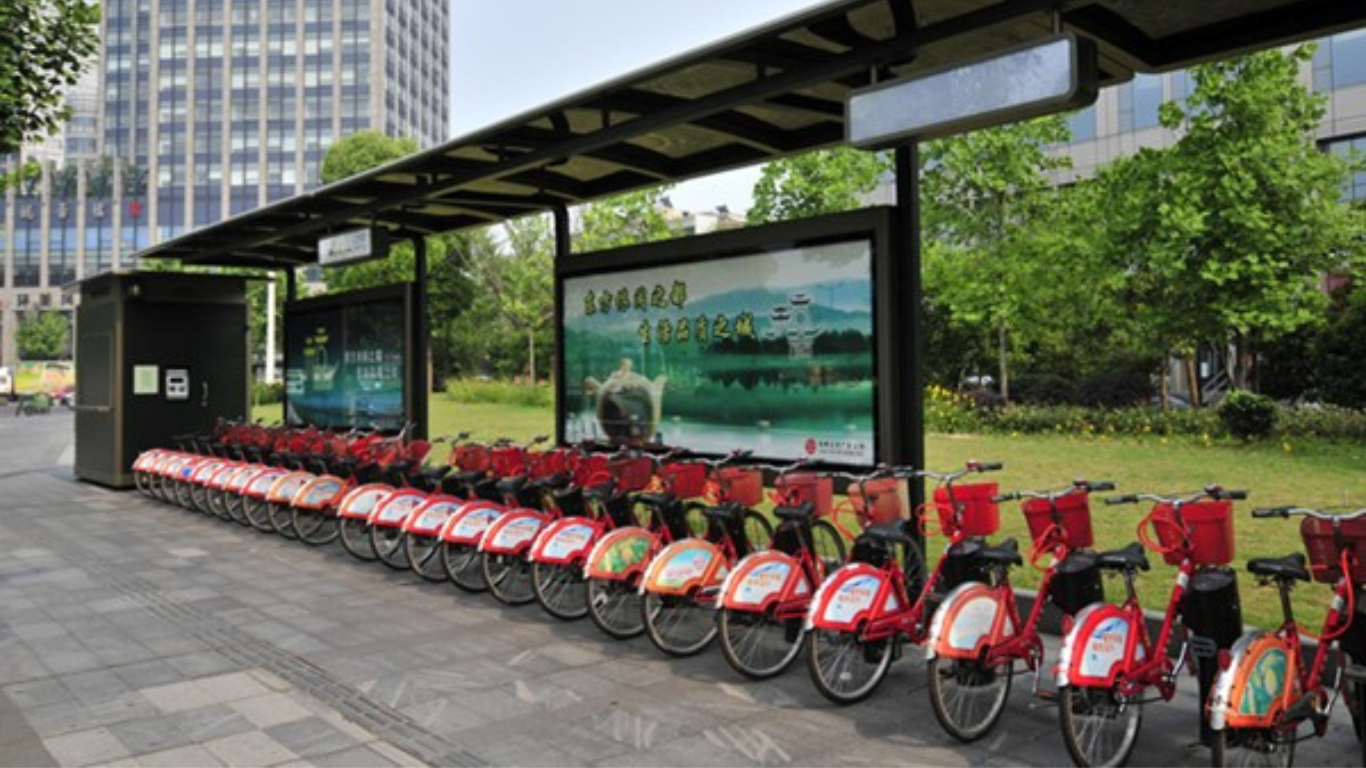
Hangzhou initiated to put the public bicycle-sharing system into operation in 2008 to overcome severe traffic congestion in the City that exhausted people. Turns out, the practice has not only overcome the challenge but has also received positive international feedbacks.
About the Initiative: Creating a New Mode of Green Travel
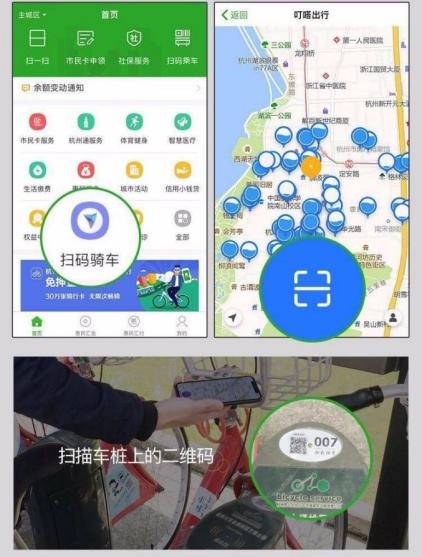
“Public Bicycle Sharing” is the first large-scale bicycle-sharing programme in China that encourages green travel. The programme proposed a new model of cooperation between the government and companies. Under the “government calls and companies manage” model, the government invests in the primary system construction, and companies are responsible for the management expenses
The business models of these companies include selling advertising space at bicycle stations and providing convenient public services at service pavilions. At the level of specific operations, Hangzhou’s public bicycle-sharing system has a real-time dynamic scheduling management mechanism and assigns people to help customers rent and return bicycles during the peak hours in the morning and evening. The programme also has its own official website, hotline, SMS, and WeChat platform to respond to the feedback of citizens.
Journey and Updates
Hangzhou’s public bicycle-sharing system has continued to develop, achieving notable success in energy saving and emission reduction. Today, Hangzhou’s public bicycle-sharing system has grown to the world’s largest public bicycle-sharing project, with a total of 116,000 public bicycles in the city and an average daily rental volume of around 250,000, with the service area and the number of public bicycles increased.
Hangzhou has also taken incremental measures in making shared bikes more convenient, such as using the QR code scan to rent and return bikes and returning bikes overnight. Different systems in different areas are interconnected, making it more convenient for citizens to travel across districts.
With the rise of private shared bicycles giving impact on Hangzhou’s public bicycle system development, the project has continued to enrich its managing model and add support facilities to achieve sustainable development.
Hangzhou public bicycle project has also been able to achieve a breakeven point by relying on bicycle service outlets to develop a variety of convenient services, such as charging, beverage vending, baby stroller rental, and express delivery storage services. Hangzhou has also equipped major roads with non-motorised lanes and built cycling greenways with a total length of about 4,073km. In addition, the project has built modes combining public transport and bicycle interchange (B+R), and park and ride (P+R) to enhance the mobility of the public’s trip modes.

In 2018, Hangzhou’s public bicycle sharing system already owned 3,111 service outlets and 78,000 bicycles and served about 300,000 people per day with a free usage rate reaching 96% and a satisfaction rate up to 95.09%. Converted to average distance traveled by riders per day in 2013, the Hangzhou public bicycle system has reduced 137,400 tons of CO2 emissions. It shows the system’s achievements in energy conservation, emission reduction, and the establishment of a low-carbon city. Meanwhile, it is instrumental in elevating the city’s image, improving the city layout, and strengthening citizens’ physical health.
Furthermore, facing the unexpected COVID-19 in 2020, Hangzhou public bicycle system ensured the enduring operation, disinfection, and maintenance, safeguarding the public’s travel needs in face of a significant reduction in public transport and providing travel services for nearly 70 million people in the first 10 months. According to data released by the C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group, from 2008 to 2020, Hangzhou’s public bicycles have been rented out a cumulative total of 1.098 billion times, equivalent to a reduction of 549 million car trips and 1.461 million tons of CO2 emissions
International Acknowledgements
Hangzhou’s “Public Bicycle Sharing” initiative has received positive international feedbacks. In 2014, the initiative won the Guangzhou International Award for Urban Innovation (the third Guangzhou Award). In the second Guangzhou Award (2014), it emerged with its effective low-carbon transport model, setting an example for public transport planning in other cities and becoming a viable initiative to achieve long-term goals of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality worldwide.
The initiative was also selected as one of the five best cycling practical cities in the world by the C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group at the Hangzhou International Day in 2021. Ying Gao, Head of Regional Coordination and Partnerships of C40 Cities, said, “This model of Hangzhou, as far as we know, has been spread to more than 300 cities around the world. Hangzhou’s construction in urban wetlands and greenways is also outstanding and is a model worth promotion and demonstration.”
Hangzhou Public Bicycle System has created dramatic environmental benefits, promoted green travel, and provided a quiet, economical, and pollution-free solution for cities to combat climate change. Hangzhou is eyeing to make this public bicycle as an important mode to travel around the city, creating a new pattern of future life and leading sharing economy and smart city.

The Guangzhou International Award for Urban Innovation (Guangzhou Award) is a global platform for city-to-city learning and the documentation, dissemination, and analysis of the local implementation of global agendas including SDGs and the New Urban Agenda (NUA). Its aim is to recognise innovation in improving social, economic, and environmental sustainability and good urban governance in cities and regions and, in so doing, to advance the prosperity and quality of life of their citizens. So far, five cycles have been held, attracting over 1,300 initiatives worldwide. The 6th Guangzhou Award is now calling for participation from all cities and local governments around the world. Please learn more at: http://www.guangzhouaward.org/The6thGuangzhouAward?lang=en











